To accommodate next-generation applications and technologies such as 5G, cloud services, 4K video, and the Internet of Things (IoT), the number, physical footprint, and bandwidth capacity of data centers worldwide are rapidly increasing. As a result, 400G has emerged as the key direction for backbone network upgrades and new infrastructure deployments.
An increasing number of data center service providers are expanding and modernizing their existing facilities to support 400G networks.
Currently, two main optical transceiver form factors are used in 400G access networks and data centers:
1. QSFP-DD, also known as QSFP56-DD, which stands for Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable Double Density
2. OSFP, short for Octal Small Form-factor Pluggable.
What is an OSFP Optical Transceiver Module?
The OSFP is a new pluggable form factor that supports eight high-speed electrical channels, initially designed to support 400Gbps (8×50G or 4×100G). It is slightly wider and deeper than QSFP-DD, but still enables up to 32 OSFP ports on a 1U front panel and delivers up to 14.4Tbps per 1U switch slot.
The OSFP module is engineered with enhanced signal integrity and thermal performance, paving the way for next-generation 800G transceivers using eight 100Gbps (8x100G) channels. This allows a seamless upgrade path from 400G to 800G. Additionally, OSFP offers backward compatibility with 100G QSFP transceivers.
What Types of 400G OSFP Optical Modules Are Available?
Below is a comprehensive comparison table of the full range of 400G OSFP modules (including some DAC/AOC cable assemblies), sorted by transmission distance from shortest to longest.
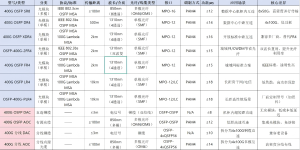
Distance-Based Selection:
0–100m: DAC / AOC / SR8 (Multi mode)
500m–2km: DR4 / XDR4 / FR4 / 2FR4 (Single-mode)
10km+: LR4 / PLR4
Medium-Based Selection:
Copper cable: DAC (no optical signal, ultra-low latency)
Multi mode fiber: SR8/AOC (short distance, low cost)
Single-mode fiber: DR4/LR4, etc. (long distance, high performance)
Special Features:
Breakout Models: Support splitting 400G into 4×100G (compatible with existing networks)
CWDM Multiplexing: 2FR4 improves fiber utilization by using dual wavelengths
Power Consumption Comparison:
Copper Cable (≤10W) < Multi mode Optical Module (≤12W) < Single-mode Long Distance (≤18W)
What are the differences between OSFP and QSFP-DD?
- MSA Definition:
OSFP is defined by the OSFP MSA, while QSFP-DD is defined by the QSFP-DD MSA alliance (QSFP56-DD). - Power Consumption:
OSFP supports higher power consumption, ranging from 12 to 15W, whereas QSFP-DD supports a lower power range of 7 to 12W. - Backward Compatibility:
QSFP-DD is more flexible in terms of backward compatibility. Because QSFP-DD shares the same size as QSFP, it can directly support 40G QSFP+, 100G QSFP28, and 200G QSFP56 modules. In contrast, OSFP modules cannot be directly plugged into QSFP-DD ports and require a passive OSFP-to-QSFP adapter for compatibility. - Thermal Design:
OSFP integrates thermal management features directly into its package design, whereas QSFP-DD does not have this feature. - Application Scenarios:
Both QSFP-DD and OSFP are suitable for data center interconnect (DCI) scenarios, including direct attach copper cables (DAC), active optical cables (AOC), and fiber optic connections.
What are the common issues or questions regarding OSFP optical modules?
- How does OSFP address thermal management requirements?
OSFP integrates a one-piece heat sink to enhance thermal dissipation efficiency, enabling modules with power consumption up to 15W to operate reliably within standard airflow environments inside switch chassis. - How is backward compatibility with QSFP achieved?
Since OSFP is slightly wider in size than QSFP, compatibility is realized through adapters. Currently, 100G QSFP modules can be installed in OSFP slots via an OSFP-to-QSFP adapter, providing backward compatibility support. - What about forward compatibility?
The thermal design of OSFP is intended to meet the anticipated heat management demands of future 800G optical modules during system and module upgrades. - What is the mission of the OSFP MSA?
The OSFP MSA is responsible for defining the OSFP technical specifications, which include standards for mechanical modules, slot architecture, electrical interfaces, pin assignments, and management interfaces. - What is the latest version of the OSFP MSA specification?
The latest version is 4.1, released on August 2, 2021. (Note: As of publicly available information in 2023, version 4.1 remains the latest. It is recommended to verify any updates on the official OSFP MSA website.) - What is the most commonly used 400G OSFP optical module type?
The most commonly used type is the OSFP SR8 model, which supports a transmission distance of up to 100 meters and uses an MPO-16 fiber interface.
