Fiber Optic Cables
-
MTP-LC Breakout Cables
MTP Female to 4xLC Duplex 8-Fiber OM3 Multimode LSZH Aqua Breakout Cable
-
MTP-LC Breakout Cables
MTP Female to 4xLC Duplex Multimode 50/125um OM4 8-Fibers Purple Color Breakout Cable
-
MTP-LC Breakout Cables
MTP Female to LC Duplex OM4 8-Fibers 40G Elite Breakout Cable
-
MTP Fiber Trunk Cables
MTP/PC to MTP/PC OM3 Multimode Low Loss IL0.35dB 24cores LSZH Aqua Color 3.0mm Trunk Cable
-
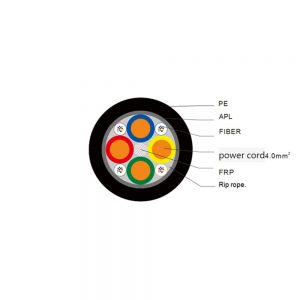
Multifiber Optic Cables
Multimode 50/125um OM3 Trunk PE Jacket Photoelectric Composite Cable, no connector
-
OM2 50/125 Multimode Fiber Optic Patch Cables
OM2 50/125um Multimode LSZH Orange Jacket duplex 2.0mm LC/UPC Optical Patchcord
-
MTP/MPO Ribbon Cables
OM3 50/125um Standard Loss LSZH Aqua Jacket Color 40G MPO Robbon Cable Patchcord
-
Outdoor Optic Multifiber Cables
Outdoor Multifiber 48-core Single-Mode SMF PE trunk Breakout Fiber Optical Cable
-
Indoor Multifiber Optic Cables
SC APC IL0.30dB 6-Cores Single-Mode SMF 5.0mmTrunk Fiber Optical Pigtail Cable
-
MPO-LC Breakout Fiber Cables
SingleMode G.657A1 MPO Cable With Fan-Out Kits to LC Duplex Connector Pre-Terminated
What Is a Fiber Optic Cable?
Fiber optic cables are network cables that transmit communication signals in the form of light pulses. The light signal may be generated by either light-emitting diodes (LEDs) or small lasers.
A fiber optic cable consists of strands of glass or optical fibers, each of which is about as thick as a human hair. Each strand has a hollow core that acts as a tunnel or a pathway for the light signals.
The core is surrounded by glass coating, also known as cladding, whose job is to reflect the light inward. That helps keep signal loss to a minimum and ensures that the light is able to navigate any bends in the cable successfully. Some cable types also feature light-absorbing dark glass in between the optical strands to prevent light leaks and cross-talk between strands.
Each individual glass fiber strand is protected by insulated casing, which is typically made of plastic. A further protective tube holds all the strands securely in place and protects them from the environment.
Fiber optic cables have many applications in various industries, as well as a number of advantages compared to standard long-distance copper cables.
Fiber Optic Cable Types
The two main types of fiber optic cables are:
- Single-mode fiber optic cables
- Multi-mode fiber optic cables
A multi-mode optical fiber cable uses LEDs to generate the light signal. Multi-mode fiber is able to transport multiple light rays — or modes — all at once. However, the different modes do not move at the same speed: the light that travels down the middle of the fiber is generally slower.
In contrast, single-mode fiber optic cables use lasers to generate light. They also feature extremely thin optical glass strands and a smaller core.
This type of cable uses a method known as Wave Division Multiplexing (WDM) to increase the amount of data traffic that each individual strand is able to carry. WDM technology combines or multiplexes light at different wavelengths and later separates or de-multiplexes it. That way, the fiber optic cable can successfully transmit a number of communication streams using a single light pulse only.
What’s more, single-mode fibers can carry light at much longer distances of up to 100 km. However, they are typically more expensive than multi-mode optical fibers.
Which fiber optic cable will work best for you would depend on many factors, including the specific application, the environment, your budget, and more.
Fiber Optic Cable Uses
Fiber optic cables have a wide variety of applications. Still, they are most common in the field of telecommunications and support most of the Internet, telephone, and cable television systems across the globe.
That’s due to the many advantages of fiber optic cable over conventional copper cabling.
To begin with, fiber optic cables have a higher capacity. A single fiber optic cable can easily support a higher network bandwidth than that of a copper wire of the same thickness. Standard fiber optic cables come in 10, 40, and 100 Gbps.
Furthermore, fiber optic cables can carry light signals over much longer distances without losing their strength. That decreases the need for signal boosters and increases the overall effectiveness of the cabling.
Finally, fiber optic cables are less prone to interference than copper network cables, which typically need to be shielded from electromagnetic interference. And even then, the shielding alone is not enough to effectively stop interference when there are a number of cables in close proximity.
All these features make fiber optic cables ideally suited for high-performance data transfer over long distances or for ensuring high-speed connections between the various parts of a building.
Fiber Optic Cable Standards
Some of the international and national bodies that set the standards for fiber optic cables include:
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
- British Standards Institution (BSI)
- Comitato Elettrotecnico Italiano (CEI)
- European Norm (EN)
- International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU)
- Norsk Elektroteknisk Komite (NEK)
- Norme Française (NF)
- Telecommunications Industry Association (TIA)
- Verband der Elektrotechnik (VDE)
Industry standards serve two main functions.
On the one hand, they provide consumers with a guarantee as to the quality and performance of the product.
On the other hand, uniform standards make it easier to identify the mechanical properties and compare the characteristics of different fiber optic cables. Among other things, that helps ensure a safe and reliable interconnection between users.
Depending on your jurisdiction, adhering to a particular standard for fiber optic cables may or may not be mandatory. To participate in major tenders in the EU, for example, it is obligatory to reference the applicable European product specification. In the US, there are different state and federal requirements, as well.
Therefore, it is essential to double-check the relevant industry requirements in your jurisdiction, as well as that of your contractors, before ordering and installing fiber optic cables.
If you have any questions regarding the standardization of our fiber optic cables or the type of cable that best fits your needs, get in touch with us. Our team will be happy to answer all your questions.